A Initial Study on Few-Shot Learning
The topic of few-shot learning (FSL) has gained more attention in recent years. To begin, let us note down several definitions that will help us in understanding the concept of FSL.
Machine learning . A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some classes of task T and performance measure P if its performance can improve with E on T measured by P. [1]
Few-Shot Learning (FSL) is a type of machine learning problems (specified by E, T and P) where E contains a little supervised information for the target T. [1]
In layman terms, few-shot learning is a learning method which employs only a small amount of data for training. A human is able to learn to recognize items after seeing it once or twice, could the same apply to these machine learning algorithms?
Motivations
I recently took part in the Huawei AI Hackathon [2] held in Stockholm from 8th to 9th November. The mission of the AI Hackathon was to design an image classification algorithms that could learn better given sets of small datasets and additional set of unlabelled dataset. There are three different datasets: 1) unlabelled dataset, 2) labelled dataset for training and 3) labelled dataset for testing with new categories. In terms of FSL, this can be termed as N-way-K-shot classification task where N denotes the number of classes and K the number of examples in each class.
The method that was experimented with was: 1) train a one-shot Siamese Network on labelled dataset to learn the similarity function between two images and consequently perform K-Nearest Neighbour to determine the class, 2) train an autoencoder with both unlabelled and labelled dataset to learn the representation and input the representations into a Deep Convolutional Neural Network for classification and 3) train a multi-task learning model with an unsupervised task on unlabelled dataset and a supervised task on labelled dataset.
In this case, we were experimenting with 3 of the methods in the taxonomy proposed by Wang. et al [1] described in the section “Taxonomy of Few-Shot Learning” below. The experiments corresponds with: 1) embedding learning method under model based learning, 2) data based method by augmenting the data with unlabelled dataset and 3) multitask learning method under model based learning respectively.
Taxonomy of Few-Shot Learning
A study was made by Wang et al, 2019 [1] on the methods and developments of Few-Shot Learning. Based on their study, they proposed the following taxonomy for the methods in this field as shown below.
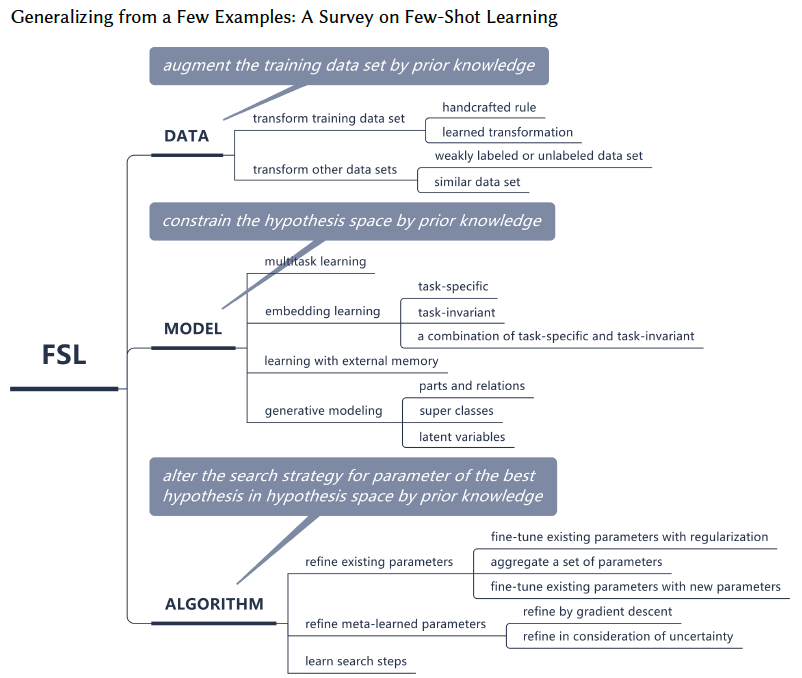
Taxonomy of Few Shot Learning
Developments in Few Shot Learning
In the recent CVPR’2019, a total of 48 accepted papers are on the topics of zero-shot to few shot learning. Reviewing some of these papers, we could likewise categorise these papers into the taxonomy proposed by [1]. In view of the Hackathon I joined and the current projects that I am working on, I reviewed some of these papers in more details as shown in the sections below.
Embedding Learning Method [Model]
Finding Task-Relevant Features for Few-Shot Learning by Category Traversal
Hongyang Li, David Eigen, Samuel Dodge, Matthew Zeiler, Xiaogang Wang
Summary
The authors of this paper has proposed introduced a novel Category Traversal Module (CTM) which traverses across the entire support set. Many of the past methods does not view the task as a whole and thus hindering it from learning task-relevant features. With the view, it is able to find dimensions that is most relevant to the task and this is a key factor for few-shot learning problems where little information is provided. Their method takes into account both the intra-class commonality and inter-class uniqueness in the feature space. CTM module selects the most relevant feature dimensions after traversing both across and within categories which makes metric learning in the subsequent feature space more effective.
Relevance
This method could be a direct application to Huawei AI Hackathon challenge. With its ability to better utilise the most useful feature dimensions, it will be able to generate better representations to perform few-shot learning and transfer learning on the new dataset with new categories.
Model-based Method
Few-Shot Adaptive Faster R-CNN
Tao Wang, Xiaopeng Zhang, Li Yuan, Jiashi Feng
Summary
The method proposed in this paper relates to the application on object detection. It aims to address the challenge in insufficient data in target domain, the challenge arising from application of few-shot learning in the domain of object detection and lastly, the risk of overadaptation. The authors introduced a pairing mechanism over source and target features to alleviate the issue of insufficient target domain examples. In addition to alleviating the issue of few examples, they proposed a bi-level module that adapts the source trained detector to the target domain: 1) the split pooling based image level adaptation module uniformly extracts and aligns paired local patch features over locations, with different scale and aspect ratio; 2) the instance level adaptation module semantically aligns paired object features while avoids inter-class confusion. A source model feature regularization (SMFR) is then applied to stabilize the adaptation process of the two modules.
Relevance
I am currently working on a research on the topic of Robustness of Vehicle Re-Identification algorithms on different datasets. The goal of this research is to study the impact of image level variations such as illuminations, viewpoints, resolutions and etc. This paper proposed a split pooling method which results in local patch features. With that, it can reflect image-level domain shifts like varied illumination, weather change, etc. This will be an interesting consideration for the research that I am currently working on.
Interesting Articles
LaSO: Label-Set Operations Networks for Multi-Label Few-Shot Learning
Amit Alfassy, Leonid Karlinsky. Amit Aides, Joseph Shtok, Sivan Harary, Rogerio Feris, Raja Giryes, Alex M. Bronstein
Multi-label dataset is an interesting domain to study in the field of few-shot learning. Many of the existing few-shot classification methods focuses on single-label data points.
References
[1] Wang, Yaqing & Yao, Quanming. (2019). Few-shot Learning: A Survey. [2] https://huawei24hourai.bemyapp.com/